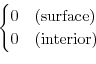|
 |
|||||||||||
 |
|
|||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||
|
Next: 3.15.3 Discrete numerical configuration Up: 3.15 Surface Driven Convection Previous: 3.15.1 Overview Contents 3.15.2 Equations solvedThe model is configured in nonhydrostatic form, that is, all terms in the Navier Stokes equations are retained and the pressure field is found, subject to appropriate bounday condintions, through inversion of a three-dimensional elliptic equation.
The implicit free surface form of the
pressure equation described in Marshall et. al Marshall et al. [1997b] is
employed. A horizontal Laplacian operator
where
Next: 3.15.3 Discrete numerical configuration Up: 3.15 Surface Driven Convection Previous: 3.15.1 Overview Contents mitgcm-support@mitgcm.org |
|||