|
|
|
|



Next: 3.16.7 Momentum equations
Up: 3.16 Customizing MITgcm
Previous: 3.16.5 Computational domain, geometry
Contents
First, because the model equations are written in terms of
perturbations, a reference thermodynamic state needs to be specified.
This is done through the 1D arrays tRef and sRef.
tRef specifies the reference potential temperature profile
(in 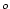 C for the ocean and C for the ocean and 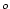 K for the atmosphere) starting
from the level k=1. Similarly, sRef specifies the reference
salinity profile (in ppt) for the ocean or the reference specific
humidity profile (in g/kg) for the atmosphere. K for the atmosphere) starting
from the level k=1. Similarly, sRef specifies the reference
salinity profile (in ppt) for the ocean or the reference specific
humidity profile (in g/kg) for the atmosphere.
The form of the equation of state is controlled by the character
variables buoyancyRelation and eosType.
buoyancyRelation is set to 'OCEANIC' by default and
needs to be set to 'ATMOSPHERIC' for atmosphere simulations.
In this case, eosType must be set to 'IDEALGAS'.
For the ocean, two forms of the equation of state are available:
linear (set eosType to 'LINEAR') and a polynomial
approximation to the full nonlinear equation ( set eosType to
'POLYNOMIAL'). In the linear case, you need to specify the
thermal and haline expansion coefficients represented by the variables
tAlpha (in K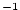 ) and sBeta (in ppt ) and sBeta (in ppt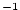 ). For
the nonlinear case, you need to generate a file of polynomial
coefficients called POLY3.COEFFS. To do this, use the program
utils/knudsen2/knudsen2.f under the model tree (a Makefile is
available in the same directory and you will need to edit the number
and the values of the vertical levels in knudsen2.f so that
they match those of your configuration). ). For
the nonlinear case, you need to generate a file of polynomial
coefficients called POLY3.COEFFS. To do this, use the program
utils/knudsen2/knudsen2.f under the model tree (a Makefile is
available in the same directory and you will need to edit the number
and the values of the vertical levels in knudsen2.f so that
they match those of your configuration).
There there are also higher polynomials for the equation of state:
- 'UNESCO':
- The UNESCO equation of state formula of
Fofonoff and Millard [15]. This equation of state
assumes in-situ temperature, which is not a model variable; its
use is therefore discouraged, and it is only listed for
completeness.
- 'JMD95Z':
- A modified UNESCO formula by Jackett and
McDougall [33], which uses the model variable potential
temperature as input. The 'Z' indicates that this equation
of state uses a horizontally and temporally constant pressure
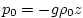 . .
- 'JMD95P':
- A modified UNESCO formula by Jackett and
McDougall [33], which uses the model variable potential
temperature as input. The 'P' indicates that this equation
of state uses the actual hydrostatic pressure of the last time
step. Lagging the pressure in this way requires an additional pickup
file for restarts.
- 'MDJWF':
- The new, more accurate and less expensive
equation of state by McDougall et al. [41]. It also
requires lagging the pressure and therefore an additional pickup
file for restarts.
For none of these options an reference profile of temperature or
salinity is required.



Next: 3.16.7 Momentum equations
Up: 3.16 Customizing MITgcm
Previous: 3.16.5 Computational domain, geometry
Contents
mitgcm-support@dev.mitgcm.org
| Copyright © 2002
Massachusetts Institute of Technology |
 |
|