|
|
|
|



Next: 6.3.5 Tapering and stability
Up: 6.3 Gent/McWiliams/Redi SGS Eddy
Previous: 6.3.3 Griffies Skew Flux
Contents
Visbeck et al., 1996, suggest making the eddy coefficient,
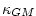 , a function of the Eady growth rate, , a function of the Eady growth rate,
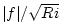 . The formula involves a non-dimensional constant, . The formula involves a non-dimensional constant,
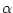 , and a length-scale , and a length-scale 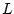 : :
where the Eady growth rate has been depth averaged (indicated by the
over-line). A local Richardson number is defined
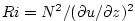 which, when combined with thermal wind gives:
where which, when combined with thermal wind gives:
where 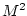 is defined is defined
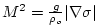 .
Substituting into the formula for .
Substituting into the formula for
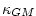 gives: gives:
mitgcm-support@dev.mitgcm.org
| Copyright © 2002
Massachusetts Institute of Technology |
 |
|