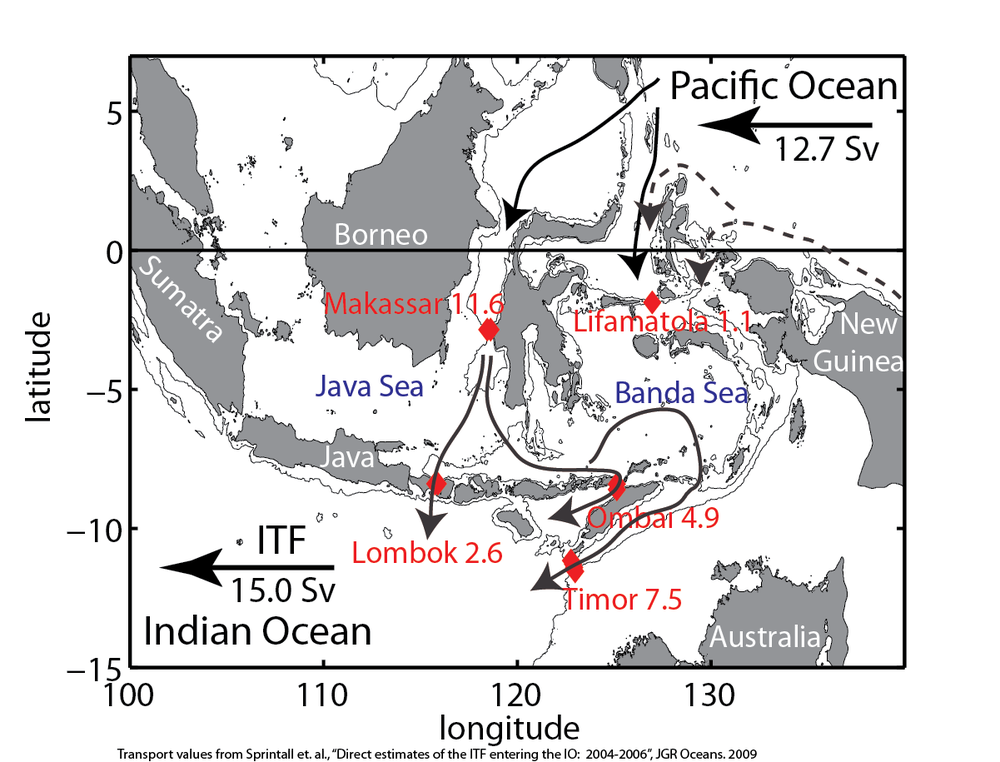
The Indonesian Through Flow (ITF) provides a low-latitude pathway for warm, fresh water to move from the Pacific to the Indian Ocean, in a key component of the ocean’s global heat conveyor belt – from a visualization of a global MITgcm simulation
story by Helen Hill

This month we spotlight work from researcher Wlademir Santis (Oceanographic Institute, University of Sao Paulo, Pça. do Oceanográfico, Brazil) and co-authors Luis Aímol (Gur Aryeh Institute for Research and Education, Cambridge, MA, USA), Paola Castellanos (Departament d’Oceanografia Física i Tecnològica, Institut de Ciències del Mar, CSIC, Barcelona, Spain) and Edmo J. D. Campos (Oceanographic Institute, University of Sao Paulo, Pça. do Oceanográfico, Brazil) who have been using MITgcm in work seeking to understand how the Indonesian Throughflow (ITF) might vary under ice age conditions.
The ITF is of particular interest because it provides a low-latitude pathway for warm, fresh water to move from the Pacific to the Indian Ocean, in a key component of the ocean’s global heat conveyor belt. Higher ocean surface topography in the western Pacific than in the Indian Ocean drives upper thermocline water from the North Pacific through the Indonesian archipelago, with the water taking the western route through the Makassar Strait passing either directly through the Java Sea to exit through the Lombok Strait or flowing eastward into the Banda Sea. Weaker flow of saltier and denser South Pacific water passes over the Lifamatola Passage and into the Banda Sea, where the water masses are mixed due to tidal effects, Ekman pumping, and heat and fresh water flux at the ocean surface. From the Banda Sea the ITF exits through the Timor, Ombai, and Lombok passages, emerging into the Indian Ocean..
In their paper The impacts of the Indonesian Throughflow on the inter-basin seesaw mechanism published in the International Journal of Climate, Santis et al. use the MITgcm in a series of topographically simplified experiments to investigate the impacts the ITF has on climate through its associated inter-basin seesaw in an idealized scenario expected in glacial periods. To reduce the complexity of the coupled system, while retaining the basic physical mechanism behind the ocean and atmospheric circulation, the team use an experimental domain stripped down to just three northern basins connected to an unblocked southern ocean, in which all continents are replaced by one-grid-wide barriers employing a coupled implementation of the ocean–atmosphere–sea ice model documented in Marshall et al. (1997a, 1997b) .

Wlademir Santis is a graduate student at the University of São Paulo in Brazil. He has been using the MITgcm since beginning his PhD 4 years ago. When he is not working with the oceans, Santis says he enjoys to go fishing with his son.
The equatorwards shift of the Southern Hemisphere westerlies found in glacial periods is understood to decrease both the Agulhas Leakage (AL) (the periodic release of warm salty water from the Agulhas Current of the eastern Indian Ocean into the Atlantic) and the thermohaline circulation (THC) in the Atlantic. Recent results have suggested that these changes are followed by an increased THC in the Pacific, through an inter-basin seesaw mechanism. The enhanced circulation in the Pacific demands thermocline water to cross the equator towards northern latitudes, which shifts the water source of the ITF from the low-salinity North Pacific to the relative saltier South Pacific.
Santis et al’s experiments indicate that in this equilibrium, the salinity anomalies of the throughflow impact the inter-basin seesaw towards the restoration of the modern climate, enhancing North Atlantic Deep Water (NADW) formation and decreasing the THC in the Pacific. Results are noted to be consistent with paleo-observations, perhaps providing new insights to interpreting the climate changes in glacial periods.
To find out more about this work contact Wlademir
This Month’s Featured Publication
- Wlademir Santis, Luis Aímol, Paola Castellanos and Edmo J. D. Campos (2018), The impacts of the Indonesian Throughflow on the inter-basin seesaw mechanism, in idealized experiments, Int. J. Climatol, doi: 10.1002/joc.5424
Other New Publications this Month
Arash Bigdeli (2017), Modeling Gas Budgets in Marginal Sea Ice Zones, Doctoral Dissertation, University of Rhode Island, pdf (digitalcommons.uri.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1698&context=oa_diss)
Quentin Carradec, Eric Pelletier, Corinne Da Silva et al (2018), A global ocean atlas of eukaryotic genes, Nature Communications, volume 9, Article number: 373, doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02342-1
Ciavatta, Stefano, R. J. W. Brewin, J. Skakala, Luca Polimene, Lee de Mora, Yuri Artioli, Icarus Allen. (2018), Assimilation of Ocean‐Color Plankton Functional Types to Improve Marine Ecosystem Simulations, Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, doi: 10.1002/2017jc013490
Andrea A. Cimatoribus, U. Lemmin, D. Bouffard, D. A. Barry (2018), Nonlinear Dynamics of the Near-Shore Boundary Layer of a Large Lake (Lake Geneva), Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, doi: 10.1002/2017JC013531
B. Drummond, N. J. Mayne, I. Baraffe, P. Tremblin, J. Manners, D. S. Amundsen, J. Goyal, and D. Acreman (2018), The effect of metallicity on the atmospheres of exoplanets with fully coupled 3D hydrodynamics, equilibrium chemistry, and radiative transfer, arXiv: 1801.01045 [Astronomy & Astrophysics]
Jordan, J, Holland, P, Goldberg, D, Snow, K, arthern, R, Campin, J-M, Heimbach, P and Jenkins, A (2017), Ocean-forced ice-shelf thinning in a synchronously coupled ice–ocean model, Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, doi: 10.1002/2017JC013251
Helga S. Huntley, Patricia Ryan (2018), Wind Effects on Flow Patterns and Net Fluxes in Density-Driven High-Latitude Channel Flow, Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, doi: 10.1002/2017JC012748
Mari Fjalstad Jensen (2017), Abrupt changes in sea ice and dynamics of Dansgaard Oeschger events, Doctoral Disertation, University of Bergen, Norway. pdf http://bora.uib.no/bitstream/handle/1956/17101/dr-thesis-2017-Mari-Fjalstad-Jensen.pdf
Meibing Jin, Clara Deal, Wieslaw Maslowski, Patricia Matrai, Andrew Roberts, Robert Osinski, Younjoo J. Lee, Marina Frants, Scott Elliott, Nicole Jeffery, Elizabeth Hunke, Shanlin Wang (2018), Effects of Model Resolution and Ocean Mixing on Forced Ice-Ocean Physical and Biogeochemical Simulations Using Global and Regional System Models, Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, doi: 10.1002/2017JC013365
Dan Jones, Gael Forget, Bablu Sinha, Simon Josey, Emma Boland, Andrew Meijers, Emily Shuckburgh (2018), Local and Remote Influences on the Heat Content of the Labrador Sea: an Adjoint Sensitivity Study, Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, doi: 10.17605/OSF.IO/KC2U9
Jennifer King, Henriette Skourup, Sine M. Hvidegaard, Anja Rösel, Sebastian Gerland, Gunnar Spreen, Chris Polashenski, Veit Helm, Glen E. Liston (2018), Comparison of Freeboard Retrieval and Ice Thickness Calculation From ALS, ASIRAS, and CryoSat-2 in the Norwegian Arctic, to Field Measurements Made During the N-ICE2015 Expedition, Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, doi: 10.1002/2017JC013233
Pushkar Kumar, Jain, Kyle Mandli, Ibrahim Hoteit, Omar Knio, ClintDawson (2018), Dynamically adaptive data-driven simulation of extreme hydrological flows, Ocean Modelling, Volume 122, February 2018, Pages 85-103, doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2017.12.004
L. Mu, Q. Yang,, M. Losch, S.N. Losa, R. Ricker, L. Nerger, X. Liang (2018), Improving sea ice thickness estimates by assimilating CryoSat‐2 and SMOS sea ice thickness data simultaneously, Quarterly Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, doi: 10.1002/qj.3225
Naila F. Raboudi, Boujemaa Ait-El-Fquih, and Ibrahim Hoteit (2018), Ensemble Kalman filtering with one-step-ahead smoothing, Monthly Weather Review, doi: 10.1175/MWR-D-17-0175.1
Simone Sammartino, José C. Sánchez-Garrido, Cristina Naranjo, Jesús García Lafuente, Pablo Rodríguez Rubio, Marcos Sotillo (2018), Water renewal in semi-enclosed basins: A high resolution lagrangian approach with application to the bay of algeciras, strait of gibraltar, Limnology and Oceanography Methods, doi: 10.1002/lom3.10231
G Sannino and A Carillo, Energy from seas and oceans, Energia, ambiente e innovazione, 2/2017, doi: 10.12910/EAI2017-030
Wlademir Santis, Luis Aímola, Paola Castellanos, Edmo J. D. Campos (2018), The impacts of the Indonesian Throughflow on the inter-basin seesaw mechanism, in idealized experiments, International Journal of Climatology, doi: 10.1002/joc.5424
Callum J. Shakespeare and Andrew McC. Hogg (2018), The life-cycle of spontaneously generated internal waves, Journal of Physical Oceanography, doi: 10.1175/JPO-D-17-0153.1
Andrew L. Stewart, Andreas Klocker, Dimitris Menemenlis (2018), Circum-Antarctic Shoreward Heat Transport Derived From an Eddy- and Tide-Resolving Simulation, Geophysical Research Letters, doi: 10.1002/2017GL075677
Jinbo Wang, Lee-Lueng Fu, Bo Qiu, Dimitris Menemenlis, Tom Farrar, Yi Chao, Andrew F. Thompson, and Mar M. Flexas (2018), An Observing System Simulation Experiment for the Calibration and Validation of the Surface Water and Ocean Topography Sea Surface Height Measurement Using In-Situ Platforms, Journal of Atmospheric and Oceanic Technology, doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-17-0076.1
Peiwen Zhang, Zhenhua Xu, Qun Li, Baoshu Yin, Yijun Hou, Antony K. Liu (2018), The evolution of mode-2 internal solitary waves modulated by background shear currents, Nonlin. Processes Geophys. Discuss., doi: 10.5194/npg-2017-78
Do you have news about research using MITgcm? We are looking for contributions to these pages. If you have an interesting MITgcm project (ocean, atmosphere, sea-ice, physics, biology or otherwise) that you want to tell people about, get in touch. To make a post, contact Helen