|
|
|
|



Next: 1.3 Continuous equations in
Up: 1.2 Illustrations of the
Previous: 1.2.8 Ocean biogeochemical cycles
Contents
Figure 1.13 shows MITgcm being used to simulate a
laboratory experiment inquiring into the dynamics of the Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC). An
initially homogeneous tank of water (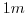 in diameter) is driven from its
free surface by a rotating heated disk. The combined action of mechanical
and thermal forcing creates a lens of fluid which becomes baroclinically
unstable. The stratification and depth of penetration of the lens is
arrested by its instability in a process analogous to that which sets the
stratification of the ACC.
in diameter) is driven from its
free surface by a rotating heated disk. The combined action of mechanical
and thermal forcing creates a lens of fluid which becomes baroclinically
unstable. The stratification and depth of penetration of the lens is
arrested by its instability in a process analogous to that which sets the
stratification of the ACC.
Figure 1.13:
A numerical simulation (left) of a 1m diameter laboratory
experiment (right) using MITgcm.
![\resizebox{7.0in}{4.5in}{
\includegraphics*[1.5in,1.5in][8.0in,8.2in]{s_overvie...
...\\
\includegraphics*[1.5in,0.5in][8.0in,8.5in]{s_overview/figs/labflow.eps}
}](img109.png)
|
mitgcm-support@mitgcm.org
| Copyright © 2006
Massachusetts Institute of Technology |
Last update 2018-01-23 |
 |
|








![\resizebox{7.0in}{4.5in}{
\includegraphics*[1.5in,1.5in][8.0in,8.2in]{s_overvie...
...\\
\includegraphics*[1.5in,0.5in][8.0in,8.5in]{s_overview/figs/labflow.eps}
}](img109.png)