|
 |
|||||||||||
 |
|
|||||||||||
 |
 |
|||||||||||
|
Next: 6.3.2 RBCS Package Up: 6.3 General purpose numerical Previous: 6.3 General purpose numerical Contents Subsections
6.3.1 OBCS: Open boundary conditions for regional modelingAuthors: Alistair Adcroft, Patrick Heimbach, Samar Katiwala, Martin Losch
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
6.3.1.4 Defining open boundary positions
There are four open boundaries (OBs), a
Northern, Southern, Eastern, and Western.
All OB locations are specified by their absolute
meridional (Northern/Southern) or zonal (Eastern/Western) indices.
Thus, for each zonal position
![]() a meridional index
a meridional index
![]() specifies the Northern/Southern OB position,
and for each meridional position
specifies the Northern/Southern OB position,
and for each meridional position
![]() , a zonal index
, a zonal index
![]() specifies the Eastern/Western OB position.
For Northern/Southern OB this defines an
specifies the Eastern/Western OB position.
For Northern/Southern OB this defines an ![]() -dimensional
``row'' array
-dimensional
``row'' array
![]() /
/
![]() ,
and an
,
and an ![]() -dimenisonal
``column'' array
-dimenisonal
``column'' array
![]() /
/
![]() Positions determined in this way allows Northern/Southern
OBs to be at variable
Positions determined in this way allows Northern/Southern
OBs to be at variable ![]() (or
(or ![]() ) positions, and Eastern/Western
OBs at variable
) positions, and Eastern/Western
OBs at variable ![]() (or
(or ![]() ) positions.
Here, indices refer to tracer points on the C-grid.
A zero (0) element in
) positions.
Here, indices refer to tracer points on the C-grid.
A zero (0) element in
![]() ,
,
![]() means there is no corresponding OB in that column/row.
For a Northern/Southern OB, the OB V point is to the South/North.
For an Eastern/Western OB, the OB U point is to the West/East.
means there is no corresponding OB in that column/row.
For a Northern/Southern OB, the OB V point is to the South/North.
For an Eastern/Western OB, the OB U point is to the West/East.
For example
OB_Jnorth(3)=34 means that:
T( 3 ,34) is a an OB point
U(3:4,34) is a an OB point
V( 4 ,34) is a an OB point
while
OB_Jsouth(3)=1 means that:
T( 3 ,1) is a an OB point
U(3:4,1) is a an OB point
V( 4 ,2) is a an OB point
For convenience, negative values for Jnorth/Ieast refer to
points relative to the Northern/Eastern edges of the model
eg.
![]() means that the point
means that the point
![]() is a northern OB.
is a northern OB.
Add special comments for case #define NONLIN_FRSURF, see obcs_ini_fixed.F
6.3.1.5 Equations and key routines
6.3.1.5.1 OBCS_READPARMS:
Set OB positions through arrays OB_Jnorth(Ny), OB_Jsouth(Ny), OB_Ieast(Nx), OB_Iwest(Nx), and runtime flags (see Table 6.3).
6.3.1.5.2 OBCS_CALC:
Top-level routine for filling values to be applied at OB for
- constant vertical
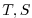 profiles as specified in file
data (tRef(Nr), sRef(Nr)) with zero velocities
profiles as specified in file
data (tRef(Nr), sRef(Nr)) with zero velocities 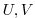 ,
,
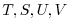 values determined via Orlanski radiation conditions
(see below),
values determined via Orlanski radiation conditions
(see below),
- prescribed time-constant or time-varying fields (see below).
6.3.1.5.3 ORLANSKI
Orlanski radiation conditions [Orlanski, 1976]
6.3.1.5.4 OBCS_PRESCRIBE_READ
Setting OB fields and updates
6.3.1.5.5 OBCS_BALANCE
6.3.1.5.6 OBCS_APPLY_*:
6.3.1.5.7 OBCS_SPONGE
Setting sponge layer characteristics
6.3.1.5.8 OB's with nonlinear free surface
6.3.1.6 Flow chart
C !CALLING SEQUENCE: c ...
6.3.1.7 OBCS diagnostics
Diagnostics output is available via the diagnostics package (see Section 7.1). Available output fields are summarized in Table 6.3.1.7.
6.3.1.8 Reference experiments
6.3.1.9 References
6.3.1.10 Experiments and tutorials that use obcs
- Ocean experiment in exp4 verification directory.
Next: 6.3.2 RBCS Package Up: 6.3 General purpose numerical Previous: 6.3 General purpose numerical Contents mitgcm-support@mitgcm.org