Recent posts
Categories
- Adjoint Modeling (6)
- Atmospheric Modeling (11)
- Biogeochemical Modeling (13)
- Climate modeling (20)
- Coupled Modeling (14)
- Lake Modeling (1)
- Model development (8)
- Model-data assimilation (19)
- Ocean modeling (83)
- Offline Modeling (9)
- Planetary Atmospheres (6)
- Sea-ice Modeling (10)
- Uncategorized (18)


 What is it about MITgcm that it spawns so many great movies? In a break with science stories, MITgcm shares 3 recent movies showcasing projects using MITgcm.
What is it about MITgcm that it spawns so many great movies? In a break with science stories, MITgcm shares 3 recent movies showcasing projects using MITgcm.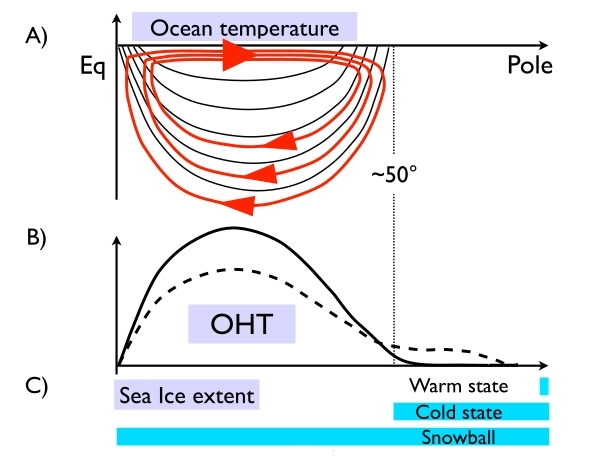 In a first for models simulating the 3d dynamics of both ocean and atmosphere, the MITgcm climate model has been found to exhibit three different stable states for exactly the same set of parameters and external forcings, suggesting that climates may exhibit multiple equilibria even in the presence of a vigorous internal variability sustained by weather systems and ocean-atmosphere-sea ice interactions…
In a first for models simulating the 3d dynamics of both ocean and atmosphere, the MITgcm climate model has been found to exhibit three different stable states for exactly the same set of parameters and external forcings, suggesting that climates may exhibit multiple equilibria even in the presence of a vigorous internal variability sustained by weather systems and ocean-atmosphere-sea ice interactions…  This month we look at work by Tom Haine, Professor of Physical Oceanography at Johns Hopkins University who is using MITgcm to model high-frequency fluctuations in the flow through the Denmark Strait…
This month we look at work by Tom Haine, Professor of Physical Oceanography at Johns Hopkins University who is using MITgcm to model high-frequency fluctuations in the flow through the Denmark Strait…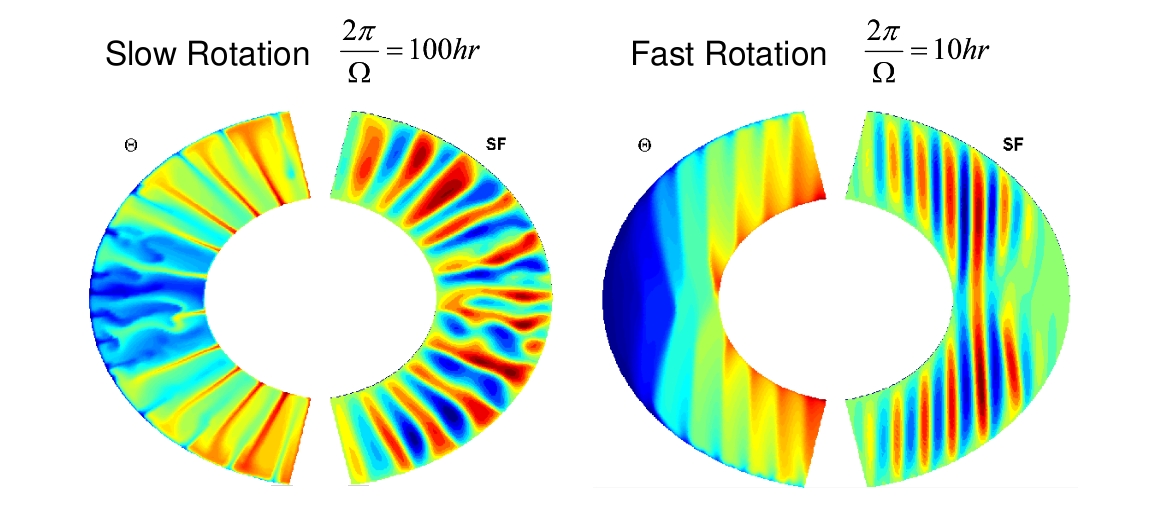 This month we look at work by Yohai Kaspi (a NOAA Climate and Global Change postdoctoral fellow currently working with Tapio Schneider at Caltech) who has been using MITgcm to model the atmosphere on a Jupiter-like gas giant…
This month we look at work by Yohai Kaspi (a NOAA Climate and Global Change postdoctoral fellow currently working with Tapio Schneider at Caltech) who has been using MITgcm to model the atmosphere on a Jupiter-like gas giant…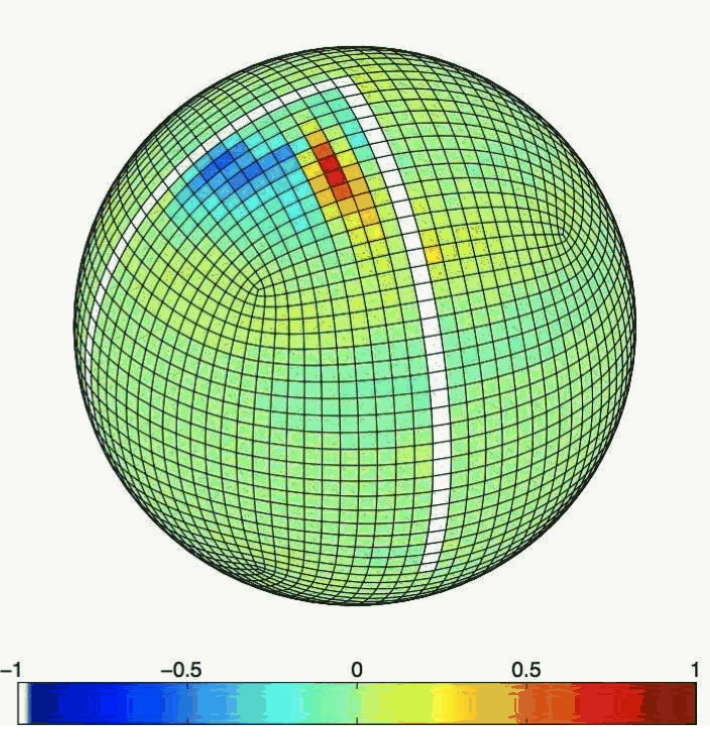 This month we look at work by Martha Buckley, David Ferreira, Jean-Michel Campin, Ross Tulloch and John Marshall, who have been using MITgcm to explore what role ocean circulation may play in Atlantic decadal variability. Asking the question: What is the role of the ocean circulation in Atlantic decadal SST variability, Buckley and co-workers use MITgcm to analyse the behavior of thermal anomalies within the framework of an idealised GCM.
This month we look at work by Martha Buckley, David Ferreira, Jean-Michel Campin, Ross Tulloch and John Marshall, who have been using MITgcm to explore what role ocean circulation may play in Atlantic decadal variability. Asking the question: What is the role of the ocean circulation in Atlantic decadal SST variability, Buckley and co-workers use MITgcm to analyse the behavior of thermal anomalies within the framework of an idealised GCM.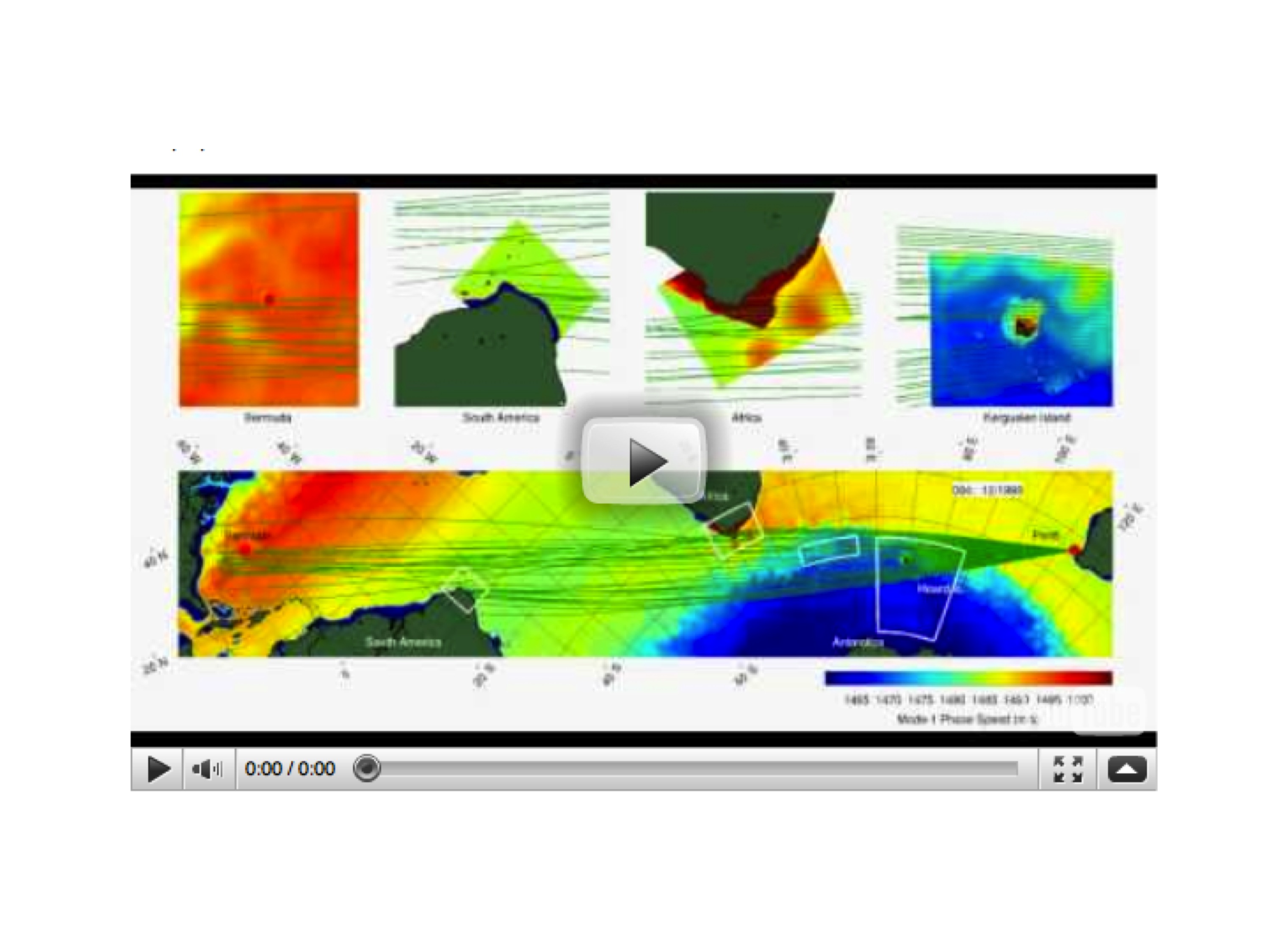 Brian Dushaw has been looking at the MITgcm ECCO2 state-estimates with help from Dimitris Menemenlis. Brian finds that by using the hydrography from the state-estimate, together with some enhanced resolution bathymetric data in key regions, he can reconstruct acoustic paths between Perth and Bermuda that were first measured in the 1960s. Previous ray-tracing efforts to reproduce this observed pathway computationally have not succeeded ….
Brian Dushaw has been looking at the MITgcm ECCO2 state-estimates with help from Dimitris Menemenlis. Brian finds that by using the hydrography from the state-estimate, together with some enhanced resolution bathymetric data in key regions, he can reconstruct acoustic paths between Perth and Bermuda that were first measured in the 1960s. Previous ray-tracing efforts to reproduce this observed pathway computationally have not succeeded ….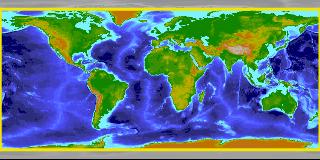 This month we focus on work by Gael Forget and the ECCO team who have been using MITgcm to construct a new ocean atlas. By using MITgcm as a means of optimally synthesising data within the framework of a physically accurate general circulation model, OCCA (short for OCean Comprehensible Atlas) provides a singularly accurate 3-year “snap-shot” of the global ocean state for the period December 2003 to November 2006…
This month we focus on work by Gael Forget and the ECCO team who have been using MITgcm to construct a new ocean atlas. By using MITgcm as a means of optimally synthesising data within the framework of a physically accurate general circulation model, OCCA (short for OCean Comprehensible Atlas) provides a singularly accurate 3-year “snap-shot” of the global ocean state for the period December 2003 to November 2006…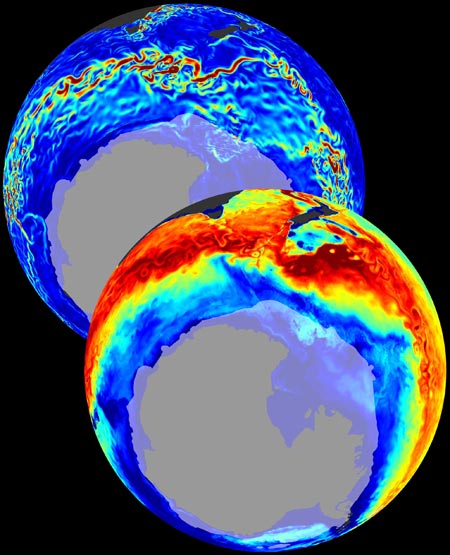 Taka Ito, Molly Woloszyn and Matt Mazloff have been studying anthropogenic CO2 transport in the Southern Ocean. Using MITgcm’s adjoint and offline capabilities, the team find a clear correlation between the pattern of carbon uptake and oceanic vertical exchange in strong support of wind-driven primary regulation of Southern Ocean ACO2 transport…
Taka Ito, Molly Woloszyn and Matt Mazloff have been studying anthropogenic CO2 transport in the Southern Ocean. Using MITgcm’s adjoint and offline capabilities, the team find a clear correlation between the pattern of carbon uptake and oceanic vertical exchange in strong support of wind-driven primary regulation of Southern Ocean ACO2 transport…