Small Storms; Big Floods: Far-Reaching Impacts
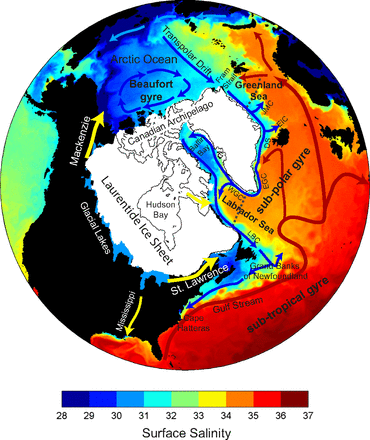 This month we focus on Alan Condron, a Research Assistant Professor in the Climate System Research Center at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, who uses MITgcm to investigate past and future climate sensitivity to changes in Arctic meltwater.
This month we focus on Alan Condron, a Research Assistant Professor in the Climate System Research Center at the University of Massachusetts Amherst, who uses MITgcm to investigate past and future climate sensitivity to changes in Arctic meltwater.
Sea – Ice Interplay
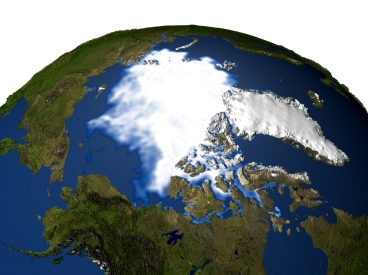 In a novel approach, MITgcmers Ian Fenty and Patrick Heimbach use optimal state and parameter estimation to improve the sea-ice simulations.
In a novel approach, MITgcmers Ian Fenty and Patrick Heimbach use optimal state and parameter estimation to improve the sea-ice simulations.
Forecasting the Weather on Pluto
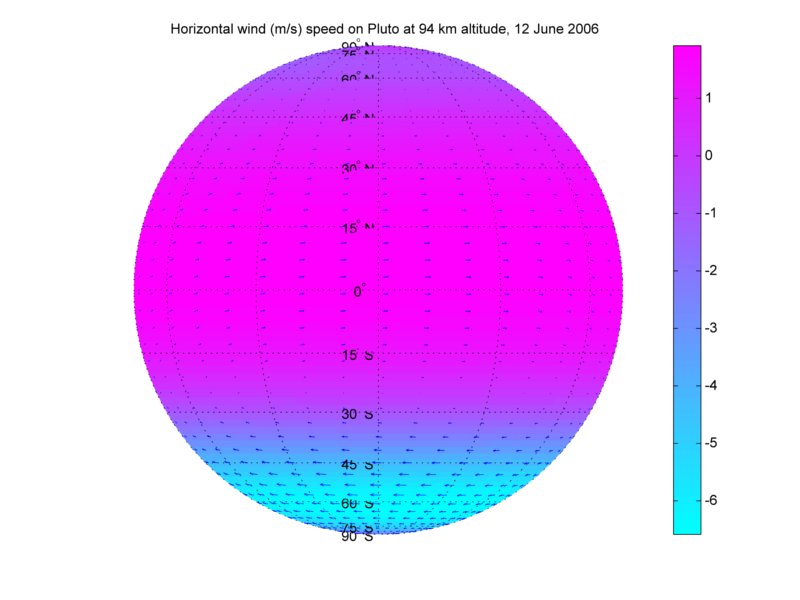 Angela Zalucha has always had a passion for weather but tantalized by the meteorology of other planetary bodies she uses MITgcm to explore the exotic atmospheres of our neighbours in the solar system and beyond, among them the recently re-defined “plutoid” Pluto.
Angela Zalucha has always had a passion for weather but tantalized by the meteorology of other planetary bodies she uses MITgcm to explore the exotic atmospheres of our neighbours in the solar system and beyond, among them the recently re-defined “plutoid” Pluto.
Arctic Carbon Cycle Modeling
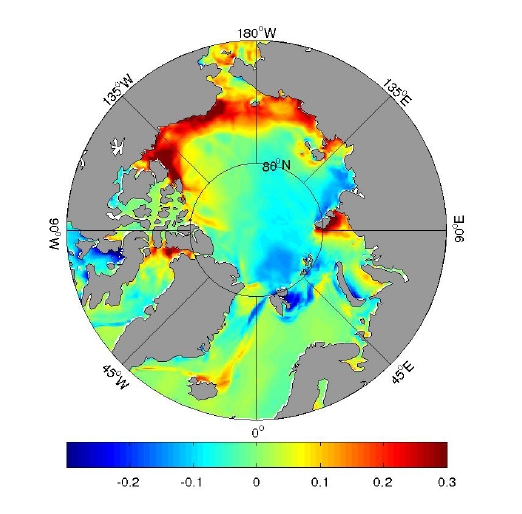 Motivated by observations indicating rapidly falling annual sea-ice minima, Manfredi Manizza and co-workers have been using an Arctic configuration of MITgcm to explore the Arctic Ocean Carbon Cycle.
Motivated by observations indicating rapidly falling annual sea-ice minima, Manfredi Manizza and co-workers have been using an Arctic configuration of MITgcm to explore the Arctic Ocean Carbon Cycle.
Climate Determinism Revisited
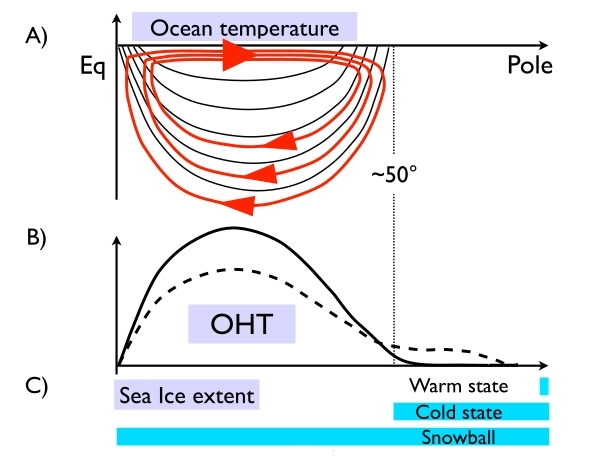 In a first for models simulating the 3d dynamics of both ocean and atmosphere, the MITgcm climate model has been found to exhibit three different stable states for exactly the same set of parameters and external forcings, suggesting that climates may exhibit multiple equilibria even in the presence of a vigorous internal variability sustained by weather systems and ocean-atmosphere-sea ice interactions…
In a first for models simulating the 3d dynamics of both ocean and atmosphere, the MITgcm climate model has been found to exhibit three different stable states for exactly the same set of parameters and external forcings, suggesting that climates may exhibit multiple equilibria even in the presence of a vigorous internal variability sustained by weather systems and ocean-atmosphere-sea ice interactions…
Modeling Nordic Seas
 This month we look at work by Tom Haine, Professor of Physical Oceanography at Johns Hopkins University who is using MITgcm to model high-frequency fluctuations in the flow through the Denmark Strait…
This month we look at work by Tom Haine, Professor of Physical Oceanography at Johns Hopkins University who is using MITgcm to model high-frequency fluctuations in the flow through the Denmark Strait…
MITjcm
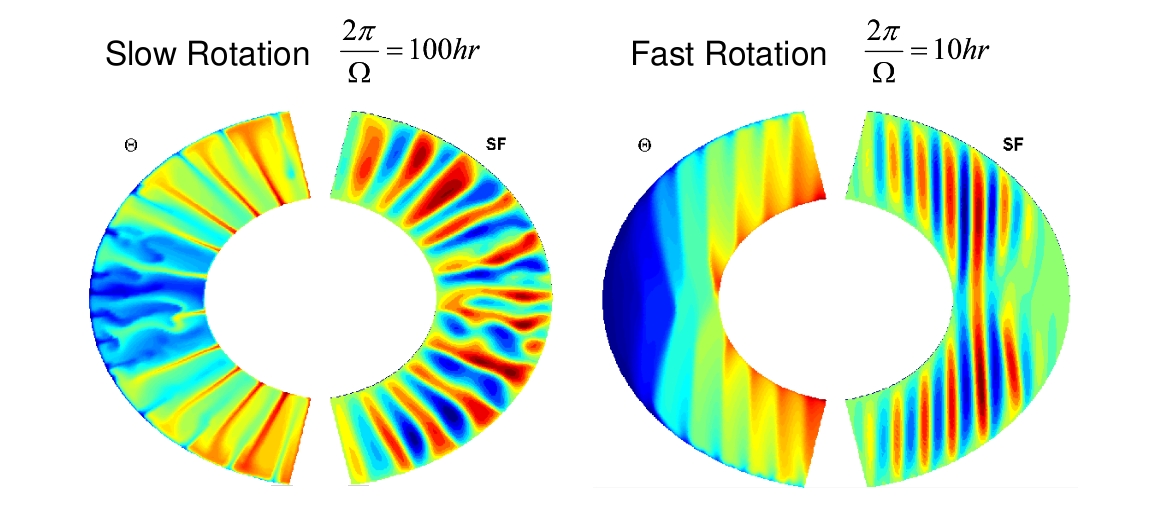 This month we look at work by Yohai Kaspi (a NOAA Climate and Global Change postdoctoral fellow currently working with Tapio Schneider at Caltech) who has been using MITgcm to model the atmosphere on a Jupiter-like gas giant…
This month we look at work by Yohai Kaspi (a NOAA Climate and Global Change postdoctoral fellow currently working with Tapio Schneider at Caltech) who has been using MITgcm to model the atmosphere on a Jupiter-like gas giant…
Ocean Circulation and Atlantic Decadal Variability
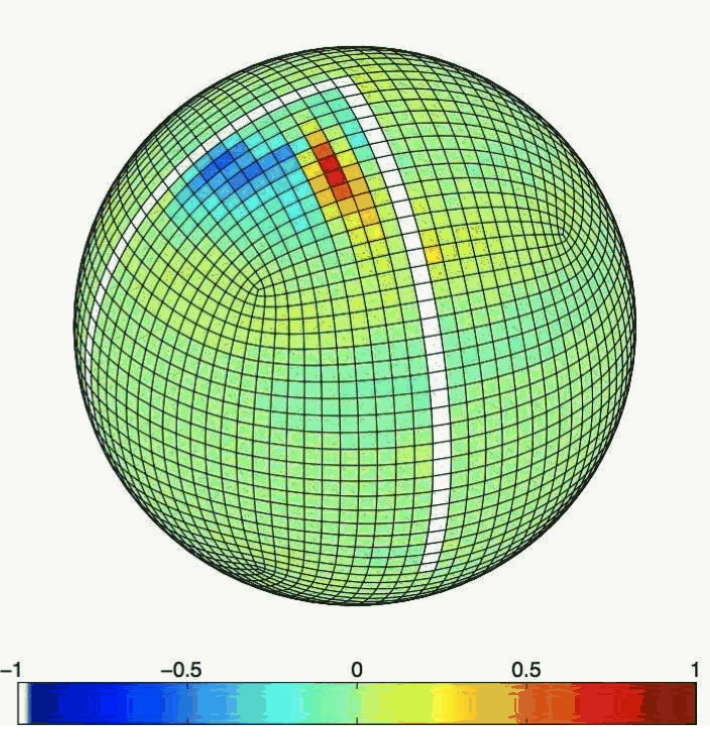 This month we look at work by Martha Buckley, David Ferreira, Jean-Michel Campin, Ross Tulloch and John Marshall, who have been using MITgcm to explore what role ocean circulation may play in Atlantic decadal variability. Asking the question: What is the role of the ocean circulation in Atlantic decadal SST variability, Buckley and co-workers use MITgcm to analyse the behavior of thermal anomalies within the framework of an idealised GCM.
This month we look at work by Martha Buckley, David Ferreira, Jean-Michel Campin, Ross Tulloch and John Marshall, who have been using MITgcm to explore what role ocean circulation may play in Atlantic decadal variability. Asking the question: What is the role of the ocean circulation in Atlantic decadal SST variability, Buckley and co-workers use MITgcm to analyse the behavior of thermal anomalies within the framework of an idealised GCM.
Sea Ice
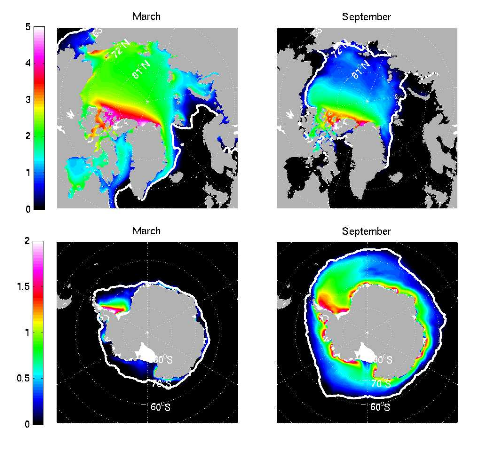 Work by Martin Losch of the Alfred-Wegener-Institute, Bremerhaven, Germany, Jean Michel Campin, Patrick Heimbach, Chris Hill (at MIT) and Dimitris Menemenlis (JPL) extending the reach of the MITgcm in to the Polar oceans, with the development of a dynamic-thermodynamic sea-ice model and its adjoint…
Work by Martin Losch of the Alfred-Wegener-Institute, Bremerhaven, Germany, Jean Michel Campin, Patrick Heimbach, Chris Hill (at MIT) and Dimitris Menemenlis (JPL) extending the reach of the MITgcm in to the Polar oceans, with the development of a dynamic-thermodynamic sea-ice model and its adjoint…
Aqua Planets
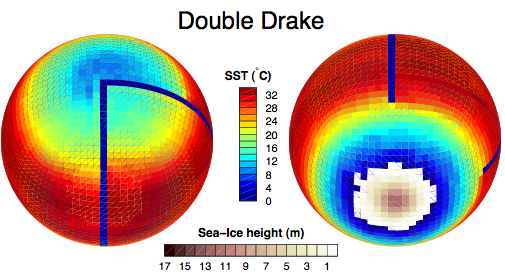 Using a coupled ocean-atmosphere version of the MITgcm to study an Earth-like planet which is entirely covered by ocean, David Ferreira and John Marshall, are exploring the elemental role of the ocean in climate…
Using a coupled ocean-atmosphere version of the MITgcm to study an Earth-like planet which is entirely covered by ocean, David Ferreira and John Marshall, are exploring the elemental role of the ocean in climate…
