Baroclinic Instability in the Ocean
![]() In a new JPO paper, Ross Tulloch, John Marshall, Chris Hill and Shafer Smith report on an observational, modeling and theoretical study of the scales, growth rates and spectral fluxes of baroclinic instability in the ocean, permitting a discussion of the relation between the instability scale, the first baroclinic deformation scale (R1) and the equilibrated eddy scale.
In a new JPO paper, Ross Tulloch, John Marshall, Chris Hill and Shafer Smith report on an observational, modeling and theoretical study of the scales, growth rates and spectral fluxes of baroclinic instability in the ocean, permitting a discussion of the relation between the instability scale, the first baroclinic deformation scale (R1) and the equilibrated eddy scale.
Arctic Carbon Cycle Modeling
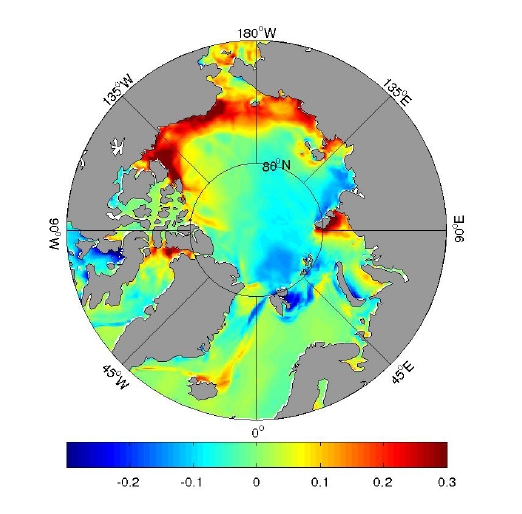 Motivated by observations indicating rapidly falling annual sea-ice minima, Manfredi Manizza and co-workers have been using an Arctic configuration of MITgcm to explore the Arctic Ocean Carbon Cycle.
Motivated by observations indicating rapidly falling annual sea-ice minima, Manfredi Manizza and co-workers have been using an Arctic configuration of MITgcm to explore the Arctic Ocean Carbon Cycle.
Climate Determinism Revisited
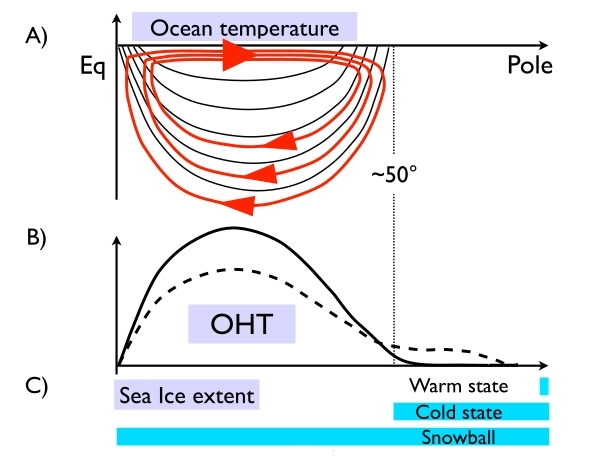 In a first for models simulating the 3d dynamics of both ocean and atmosphere, the MITgcm climate model has been found to exhibit three different stable states for exactly the same set of parameters and external forcings, suggesting that climates may exhibit multiple equilibria even in the presence of a vigorous internal variability sustained by weather systems and ocean-atmosphere-sea ice interactions…
In a first for models simulating the 3d dynamics of both ocean and atmosphere, the MITgcm climate model has been found to exhibit three different stable states for exactly the same set of parameters and external forcings, suggesting that climates may exhibit multiple equilibria even in the presence of a vigorous internal variability sustained by weather systems and ocean-atmosphere-sea ice interactions…
Modeling Nordic Seas
 This month we look at work by Tom Haine, Professor of Physical Oceanography at Johns Hopkins University who is using MITgcm to model high-frequency fluctuations in the flow through the Denmark Strait…
This month we look at work by Tom Haine, Professor of Physical Oceanography at Johns Hopkins University who is using MITgcm to model high-frequency fluctuations in the flow through the Denmark Strait…
MITjcm
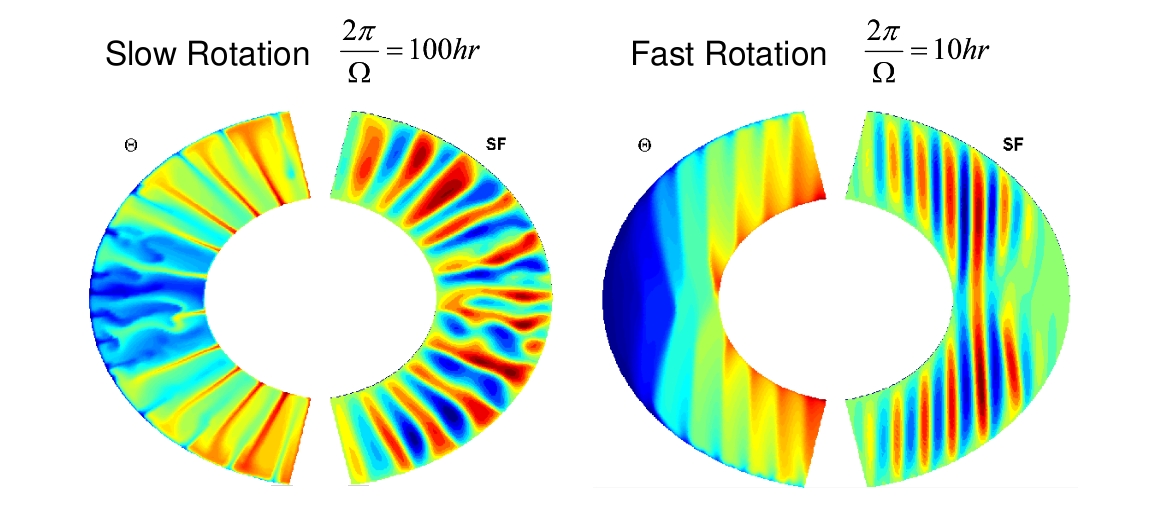 This month we look at work by Yohai Kaspi (a NOAA Climate and Global Change postdoctoral fellow currently working with Tapio Schneider at Caltech) who has been using MITgcm to model the atmosphere on a Jupiter-like gas giant…
This month we look at work by Yohai Kaspi (a NOAA Climate and Global Change postdoctoral fellow currently working with Tapio Schneider at Caltech) who has been using MITgcm to model the atmosphere on a Jupiter-like gas giant…
Ocean Circulation and Atlantic Decadal Variability
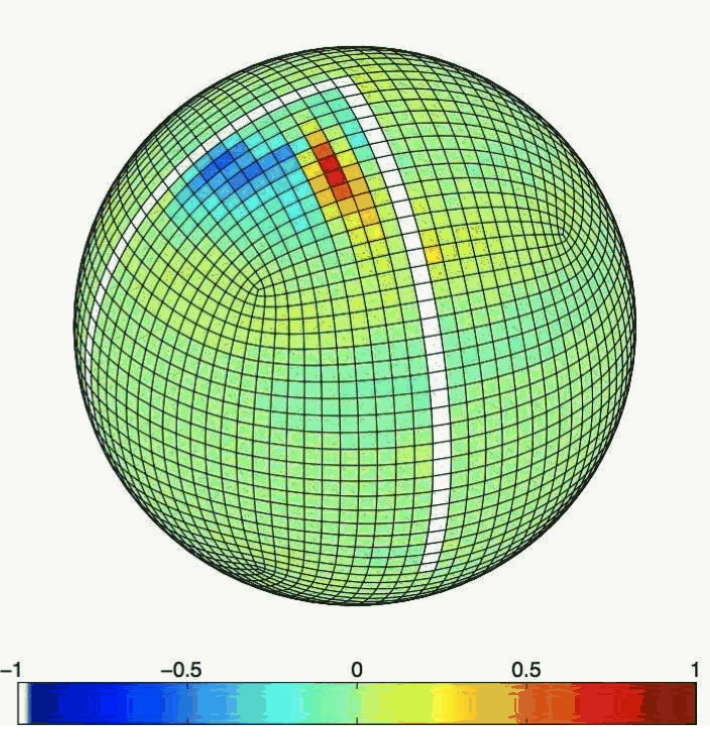 This month we look at work by Martha Buckley, David Ferreira, Jean-Michel Campin, Ross Tulloch and John Marshall, who have been using MITgcm to explore what role ocean circulation may play in Atlantic decadal variability. Asking the question: What is the role of the ocean circulation in Atlantic decadal SST variability, Buckley and co-workers use MITgcm to analyse the behavior of thermal anomalies within the framework of an idealised GCM.
This month we look at work by Martha Buckley, David Ferreira, Jean-Michel Campin, Ross Tulloch and John Marshall, who have been using MITgcm to explore what role ocean circulation may play in Atlantic decadal variability. Asking the question: What is the role of the ocean circulation in Atlantic decadal SST variability, Buckley and co-workers use MITgcm to analyse the behavior of thermal anomalies within the framework of an idealised GCM.
OCCA
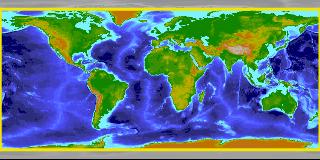 This month we focus on work by Gael Forget and the ECCO team who have been using MITgcm to construct a new ocean atlas. By using MITgcm as a means of optimally synthesising data within the framework of a physically accurate general circulation model, OCCA (short for OCean Comprehensible Atlas) provides a singularly accurate 3-year “snap-shot” of the global ocean state for the period December 2003 to November 2006…
This month we focus on work by Gael Forget and the ECCO team who have been using MITgcm to construct a new ocean atlas. By using MITgcm as a means of optimally synthesising data within the framework of a physically accurate general circulation model, OCCA (short for OCean Comprehensible Atlas) provides a singularly accurate 3-year “snap-shot” of the global ocean state for the period December 2003 to November 2006…
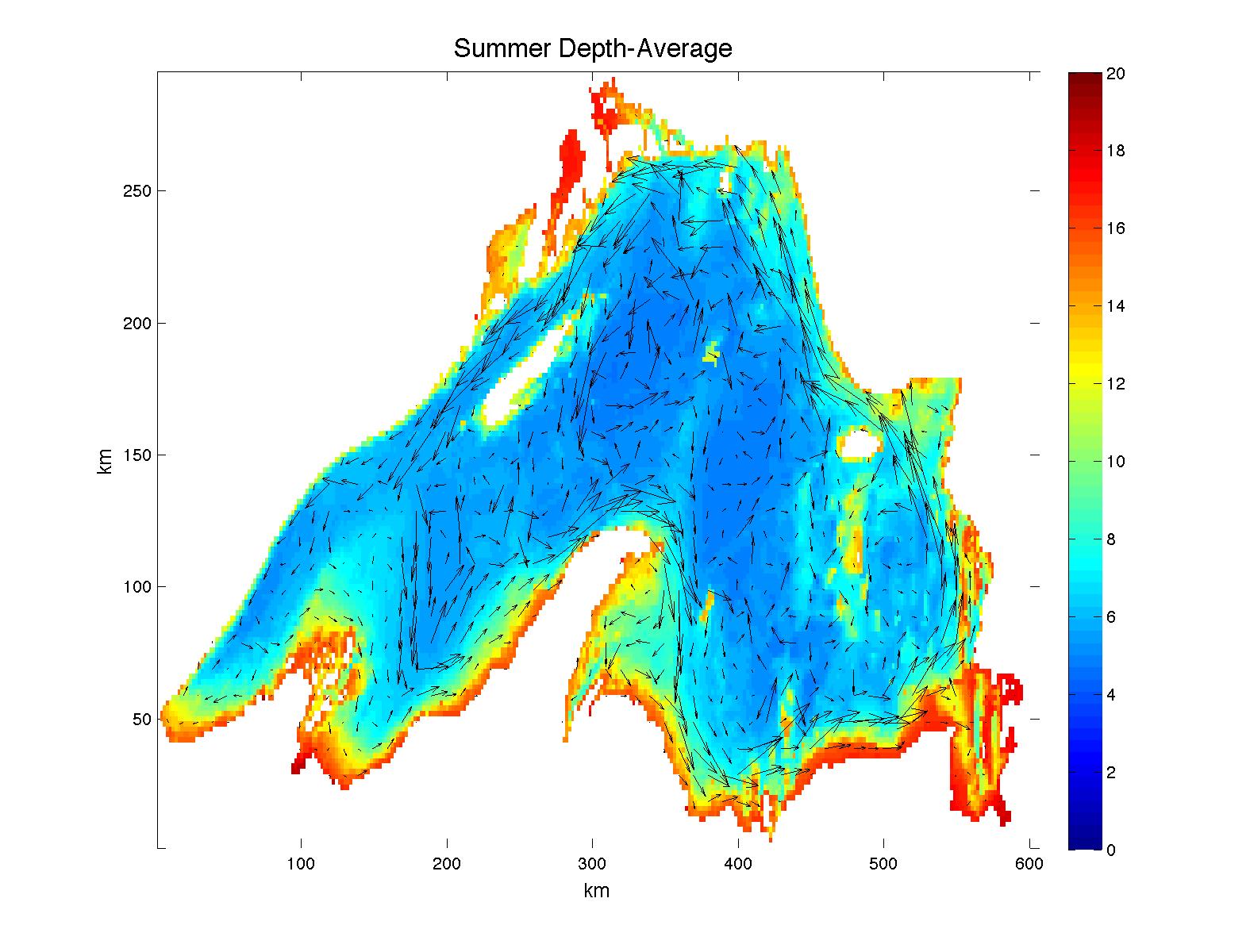
Lake Modeling
Work by Galen McKinley and Val Bennington at the University of Wisconsin, Madison using MITgcm to model the general circulation of Lake Superior as part of a project to develop a quantitative understanding of the role such bodies of water may play in the terrestrial carbon cycle…